How the life cycle of an industrial or IT project take place?
To understand what a design review is in the product innovation, whether it is engineering, industry or IT, at first it is necessary to study the progress of the product or service cycle, for instance.
To start the production of an IT solution, several successive steps of the development cycle have to be fulfilled. Each one validating the next.
Among those steps, we find the project conception in which all the hypothesis and objectives are suggested. Then follows a feasibility study. Next come the development phases and the tests of the first versions of the project, before starting the production. When the IT solution production is done, it is delivered to the user, then manage by a technical support team. Finally, the last step in the life cycle of the solution is the switch off, the end of the production and the archiving.
In the industry as in the engineering design domains the life cycles have integrated design reviews, regarding both technical aspects and audits, all carried out between every step of the process. Following this path, engineering has been able to create several levels of validation in the development cycles to ensure the success of a project, from the conception phase to the switch off.
Design review: technical aspects and audits phases
In a design review, between analysis phases it exist needs and spec sheets writing, intermediary milestones as configuration check (SRR: System Requirements Review), System Design Review (SDR) and the System Functional Review (SFR). Those milestones will allow to begin a project, gather all the client requirements and needs to finally validate one of the first conceptions of a project.
Between the specs writing and the conception, a Preliminary Design Review (PDR) is achieved enabling the validation of the project potential performances.
Before the implementation, a Critical Design Review (CDR) is applied allowing the validation of the final conception ending the conception step.
A Test Readiness Review (TRR) is carried out to validate the launch of official tests and ending the project development step at the same time.
In anticipation of the last deployment and switch off steps of the solution, a Functional Configuration Audit (FCA) and a System Verification Review (SVR) are achieved thus ending the tests phase.
How VR provide the best results to design reviews?
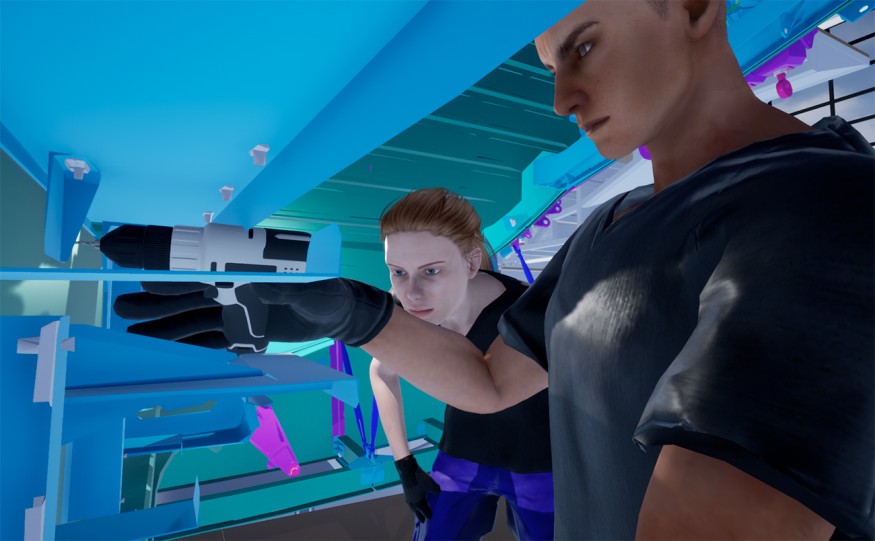
Design reviews are opportunities for teams to share information, datas and feedbacks to go further in the realization of a project. Here the objective is to validate a model based on common information by identifying the potential dysfunctionments (during or after the production) to apply rectifications or to redefine the priorities during the conception of the project.
That’s precisely what VR allows for a long time, offering the user collaboratives experiences in global VR thanks to conception tools, tagging, annotations and differents modes of interaction and expression between operators.
Virtual reality will provide to design review a lot more efficiency at every step of the project. Whether it is the initial conception, the feasibility study, the development, the tests until the beginning of the production. The time constraint hardly no longer exists in the realization of an engineering project including a predefined budget when the development cycle is done in VR. All the manipulations, tests, analysis, and the revisions applied or issued by the operators in a virtual environment are nearly infinite. That flexibility will allow if necessary to adjust the conception of a project or to repeat if needed every steps of the development cycle.
Thus, the understanding of the intention of the existing conception at the heart of the project will be facilitated, as will design reviews taking place between each phase of the project lifecycle.
The use of VR in the realization of design reviews has many benefits:
- A better estimate of the potential time overruns and therefore the costs associated with the realization of the project
- More anticipation on the conception issues
- A smoother communication and transmission of strategic information between operators
- Improving the vision of the project over time, during the different phases of the development cycle.