“Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) have the potential to become the next big computing platform, and as we saw with the PC and smartphone, we expect new markets to be created and existing markets to be disrupted.” The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc.
That is said. Virtual reality seems to be heading for a bright future in the years to come and we can hardly perceive the first glimmers.
Indeed, the VR market is booming and the economic outlook is immense. Again, The Goldman Sachs Group, plans by 2020 the adoption of VR engineering solutions in the workplace among a million users. This figure will be multiplied by 3 in 5 years to reach about 3.5 million users by 2025.
AR & VR market
The estimates augured happy days for the software and equipment editors of VRs and ARs. Indeed, the global industry could represent more than 80 billion dollars by 2025, reckons Goldman Sachs.
The distribution would be $35 billion allocated to software publishers and $45 billion allocated to virtual reality equipment manufacturers.
In terms of program, revenue from consumer-generated both Augmented Reality Softwares and Virtual Reality Softwares is estimated at 60%. The remaining 40% would be attributable to businesses and the public sector.
In terms of content, video games would be the first consumer market to develop its offer significantly, followed by real estate, retail and health.
As for equipment, 4 devices used to experience virtual reality and augmented reality would stand out: virtual reality headsets, host systems, tracking systems and controllers.
The ranking of the top three markets in terms of money supply would be in order, the video game market estimated at $11.6 billion, followed by the live events market estimated at $4.1 billion and finally the market video entertainment at $3.2 billion.
The widespread adoption of VR seems to have been preordained
It’s obvious, VR technologies will gradually improve. Problems related to cumbersome equipment, the need to introduce more mobility, but also the longer life of the batteries, are also decisive factors for the use of VR in a professional environment.
For Marjorie Perrissin-Fabert (Accenture), it exists 3 possible scenarios in the future of virtual reality and its technologies:
- A first scenario in which the evolution of VR would follow the pace of adoption of tablets in the early 2010s.
- A second rather close to the video game market, but which ultimately concerns a rather specific part of the population.
- A third scenario representative of the smartphone market when it exploded, with today a rate of adoption in France of more than 7 users out of 10 (73%).
It is also through the diversity of VR content offerings and their accessibility via smartphones that opportunities in the VR market are likely to pass and that adoption among both individuals and professionals will be wider.
VR Market : State of virtual reality among the general public and professionals
Although VR technologies are still not widely used, and especially in the workplace, they have undisputed financial potential. Accenture, having conducted a study at the end of 2016 with 26,000 users (in 26 countries), estimated that 4% of users had their own equipment and 10% were considering buying their own equipment within the next 10 months. A majority of analysts including IDC, estimate that the VR market will reach a value close to $ 17 billion by the end of 2018.
Investment costs, but also because of the lack of VR content. And it is here, in particular, that there is a strategic angle of penetration of the VR market. VR content publishers know that tomorrow they will have to be able to respond to a wide variety of requests. Many professional circles will be eager to develop their business based on virtual reality solutions.
The first cases of use occurred in the field of virtual reality were related to video games and entertainment.
Where one would have thought, at first glance, that the technology would be of interest only for a playful use, studies have revealed that learning by VR also represented a point of strong interest with 40% of VR solutions users.
Clearly, a need for more “serious” use of VR technologies actually exists. Transportation, automotive industry and medical services are among the first sectors to launch programs based on VR solutions to meet their needs, for example.
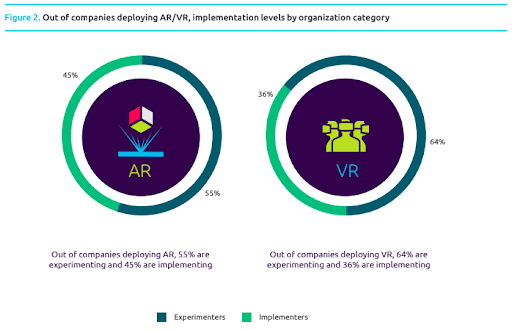
Virtual reality : between implementation complexity and direct benefits
Of course, the integration of augmented reality solutions is stronger today in companies than virtual reality. But on the other hand, experimenting with VR solutions takes precedence over AR. This shows a certain interest for the VR and its market, probably because of the opportunities for economic development that companies see there, but probably also because of the (wide) spectrum of possibilities, still not completely known, that the VR solutions seem to have to offer.
(Source : Capgemini Research Institute. 2018)
On average, 82% of companies implementing AR and VR technologies report that the benefits of these initiatives meet or exceed their expectations. Thus, at least 75% of companies that have implemented these solutions on a large scale attest to operating advantages of more than 10%.
(Source : Capgemini Research Institute. 2018)
The promise of VR, whose first benefits are beginning to be palpable, seems on track. And concretely, the examples of projects launched and companies already heavily involved are not lacking.
In China, in the health sector, teams modeled 3D liver tumor on the basis of 2D radiographs, in order to better analyze it to perform the ablation surgery. In the field of health too, exploration of the human body by dissection can be done via a VR solution with identical reproduction of a real situation.
Training is one of the most promising sectors since many cases already exist thanks to VR training program (distance learning, repetition of movement, simulation, etc.).
Risk sectors are also concerned. The British army has already put soldiers in situation on a virtual battle zone, in order to have an optimal preparation and to be able to anticipate many scenarios once in real situation. Interventions at nuclear sites also carry many risks because of the radioactivity of the intervention zones. Upstream training will be preferred, on the basis of simulations in virtual reality, before intervention on site.